Assessment of competitiveness of search queries for different variations of search results

Assessment of the degree of competition for the keyword is one of the sacred tasks of search engine optimization. Hope to discover unnoticed by competitors request with good conversion akin to the search for philosophy stone. And we will try to contribute to this alchemical party.
It turns out that the degree of competition is possible almost instantly to evaluate just by comparing the search results of two related queries – without any analysis puzomerok, sites of competitors, statistics, cost per click and shoveling the mountains of information.
Background
The difficulty of promotion in the TOP for a given keyword rightly associated with the number of competitors vying for first place. Ways of assessing this the "difficulties", there are several. Here are the most common of them.
analysis of the ranking factors. This method consists in the analysis of the SERPs and websites, it incoming: the total number of sites, contextual advertising, the average number of links, the degree of optimization of each site etc., Then this information using the weight function boils down to one indicator, KEI (Keyword Effectiveness Index), which compares the queries. The main problems of the application of this method consist in the selection of the indicators, methods for their (automatic) dimensions and weights. Just note that Google uses to rank PCs 800 count non-trivial parameters.
analysis of the rates of contextual advertising. This method is to evaluate and compare auction rates pay-per-click contextual advertising systems (Yandex Direct, Google AdWords). The connection is clear – the "interesting" request, the more advertisers are fighting for first place, the higher the rate. But the principles of pricing in the context of search engine optimization are different, which may affect the accuracy of estimates.
Compared to competitive budgets. This information is available in numerous systems of automatic promotion (SeoPult, Rookee) as the statistics of its users. But the problem is that midrange and low-frequency queries such statistics may not be enough, so often can be seen as estimates of the cost of a standard minimum amount. In addition, the main (if not only) component of this budget is the reference budget. And links to now playing a lesser role.
the Idea
But there is another interesting method based on some properties of the query language of search engines. In this language there are usually concepts such as broad and exact queries. Their meaning is that in response to a broad query, you can obtain information in all forms and with any order of the words, and in response to exact – just in the way the query is formed.
For example, in the notation of the search language Yandex broad query will look like
the
[buy a car]And accurate
the
["!to buy !the car"]
The main requirements for search engine optimization are the availability of exact occurrences of the search query in the text and layout of the website, and use them as external anchors and internal links. As a result, the site is optimized for a specific query differs from a non-optimized a large number of exact occurrences of the search query.
If the query is highly competitive, the difference in the results for broad and exact keywords will be different is irrelevant because optimized sites quite a lot and search algorithm there are plenty to choose from. If the request is low competitive, the lack of optimized search algorithm would be to compensate the rest — those that can detect words that are close to the search query, but perhaps in a different morphology and in different order.
As example, take the offhand several different queries from automotive topics (in order obviously to ensure a different degree of competition) and see what happens to them in Yandex.
Broad and exact shape of these requests, as well as the frequency of the broad queries are as follows:
the
[crossover] ["!crossover"] (239 714) [Mitsubishi Outlander] ["!Mitsubishi !Outlander"] (73 760) [Mitsubishi Outlander] ["!Mitsubishi !Outlander"] (68 149) [Mitsubishi Outlander a] ["!Mitsubishi !the Outlander"] (128) [mitsubishi outlander] ["!mitsubishi !outlander"] (41 392)
Here are the results of ranking for those searches. Here the color indicates the sites matching your search results for broad and exact options.
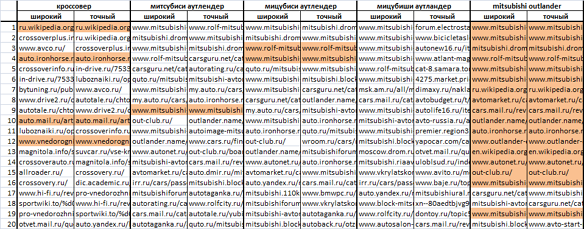
The naked eye can see the difference between [mitsubishi outlander] (41 392) and the [Mitsubishi the Outlander] (128) – that is, between requests with obviously different competition.
Calculation
Visually, the message is clear – the greater the difference between search results for broad and exact forms of a search query, the lower the competition. Variety than the lower – the competition is higher. But now how to calculate this? How to measure the extent of this diversity?
Use this expression for the distance between the rankings obtained in the work the assessment of the variability of search results.
Examples of calculations this expression can be viewed here.
So, we have the following formula to calculate the weighted relative distance between two rankings R’ and R’
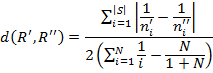
Here:
the N — the length of the rating (TOP5, TOP10, etc.);
|S| number of elements in a set S = R’ U R’, that is, the total number of unique objects in two rankings;
the n’i and n’i positions of i-th element, respectively, in the ranking R’ and R’, and if the object is not in the ranking, its position in the ranking is taken for N+1.
The higher the variety of issue, the greater the distance between the ratings. Therefore, as the degree of competition will use the value of the opposing distance:
the Cn = 1 — d
For our query we get the following values of the degree of competition (in percentage) by rating of TOP100.
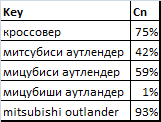
The question now is how deep to view search results. To answer this question it will help us the dependence of the degree of competition on the length of the rating presented in the following graph.
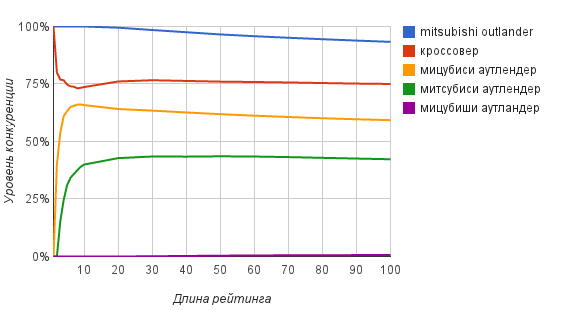
As the graph shows, at the level of TOP20-ТОП30 is possible to obtain reasonably accurate estimates of the degree of competition.
Testing
What is the method of evaluating the degree of competition more accurately reflects the costs of reaching the top search rankings? I don't know the answer to this question. As I do not know the answer to simple questions – how do you count the actual cost of SEO. Or at least the actual cost of optimization for a specific (separate) key request.
As it is possible to assess the accuracy of the forecast values, which we are not able to measure it?
The situation in dietetics: you can think of a bunch of diets, but to really assess that impact on life expectancy and will not work. And in the same way as in dietetics, I guess, to answer only on the experience of many generations.
So far, the only way to check the accuracy of the proposed method is common sense and comparison with peers. Well, simplicity and convenience he has no competitors. Because it can evaluate even for newly appeared key phrases (note to those who earns on trends)!
As for analogues, below presents a comparative evaluation of the degree of competition using some of the previously listed methods.
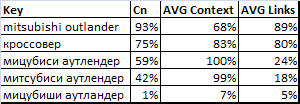
Here:
Cn – evaluation of the degree of competition obtained with our method.
AVG Context – the evaluation obtained according to the statistics of pay-per-click contextual advertising systems (Yandex Direct and Google AdWords). The values averaged and normalized (over 100% of their maximum cost per click).
AVG Links – the evaluation obtained in the systems of automatic promotion (SeoPult, SeoPult PRO, Rookee) in the recommended budget. The values averaged and normalized (over 100% of their maximum budget).
Although the values diverge, but the important thing is that the rank order when the use of estimates Cn and AVG Links is the same. It's hard to say which of the two estimates more precise, but in the original data SeoPult PRO in three queries out of five stats were missing (suggested minimum possible budget system). So there is every reason to believe that our algorithm can cope with this task better.
As for the forecast for the context rates AVG Context, he clearly stands out from the General trend. To use this method very carefully.
Opinion
The simplicity of the proposed method is obvious. The accuracy of the calculations is quite good. Plus the ability to assess in situations where other methods are powerless.
What else is needed to adequately meet the
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий