Japan offers an alternative to GPS with centimeter resolution
 the Japanese company Mitsubishi Electric has announced its intention to launch into orbit satellite constellation, which after 2018 will provide high-precision geopositioning. According to the authors ideas, with improving the accuracy of coordinate possibilities of applications of satellite navigation in practical tasks. For example, robotic cars can definitely go on your lane, knowing the coordinates of road markings.
the Japanese company Mitsubishi Electric has announced its intention to launch into orbit satellite constellation, which after 2018 will provide high-precision geopositioning. According to the authors ideas, with improving the accuracy of coordinate possibilities of applications of satellite navigation in practical tasks. For example, robotic cars can definitely go on your lane, knowing the coordinates of road markings.System Quazi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) designed to complement the American GPS in Japan. The QZSS satellites will allow calculate the receiver location with an accuracy of 1-3 cm.
"GPS positioning can give an error up to 10 meters due to various types of errors, says Yuki Sato, a research engineer of the research division of Advanced Technology R&D Center in Mitsubishi Electric. — and in Japan the GPS signal is often blocked by mountains and skyscrapers, so in many places it is just not available." Indeed, between skyscrapers in Central Tokyo to catch him is virtually impossible.
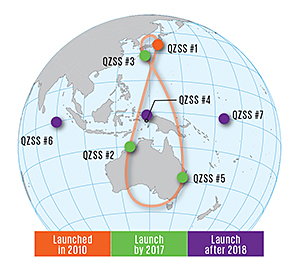
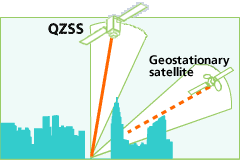 Company Mitsubishi Electric is responsible for virtually all the "space" part of the project, including manufactures satellites. Japan aerospace exploration Agency (JAXA) launched the first QZSS satellite in September 2010. Three things will launch before the end of 2017, and then the last three. It's enough excess to cover the entire country and surrounding area. From the point of view of an observer on earth, the satellites in the sky will form a shape resembling an asymmetrical figure eight. At least one satellite in geosynchronous orbit is always quasisoliton position, that is, with elevation angle more than 70°. It's critically important for residents of big cities.
Company Mitsubishi Electric is responsible for virtually all the "space" part of the project, including manufactures satellites. Japan aerospace exploration Agency (JAXA) launched the first QZSS satellite in September 2010. Three things will launch before the end of 2017, and then the last three. It's enough excess to cover the entire country and surrounding area. From the point of view of an observer on earth, the satellites in the sky will form a shape resembling an asymmetrical figure eight. At least one satellite in geosynchronous orbit is always quasisoliton position, that is, with elevation angle more than 70°. It's critically important for residents of big cities.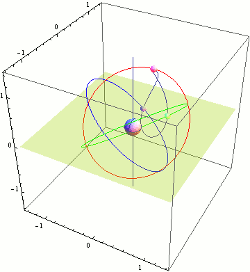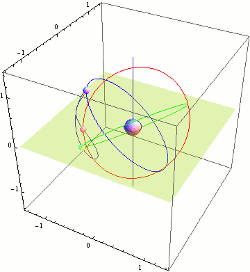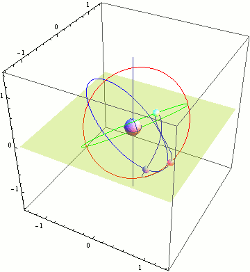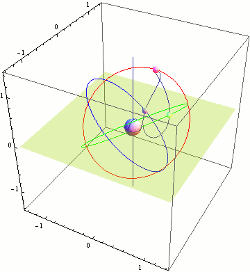 the Government of Japan has allocated $500 million for the first three satellites, as well as $1.2 billion for the construction of 1200 reference stations on the ground.
the Government of Japan has allocated $500 million for the first three satellites, as well as $1.2 billion for the construction of 1200 reference stations on the ground. Management of ground stations is entrusted to a private company Quazi-Zenith Satellite System Services designed specifically for this purpose.
The QZSS satellites are equipped with atomic clocks based on rubidium. To correct inaccuracies in triangulation control station continuously monitors the readings from the satellite and its actual location relative to the reference stations. Then the satellite information is transmitted for correction. According to engineers, the system requires constant correction so that the satellite broadcast flow rate of 2 Kbit/s.
Tests of the first satellite QZS-1 pokazalithat after the correction it provides positioning accuracy with an error of not more than 1.3 cm in the horizontal direction and 2.9 cm in the vertical. A precise navigation system can be used, for example, automatic movement of automobiles and agricultural machinery.
Mitsubishi Electric emphasizes low cost QZSS, compared with other systems of satellite positioning. For example, the budget of Galileo has already exceeded $6.9 billion
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий